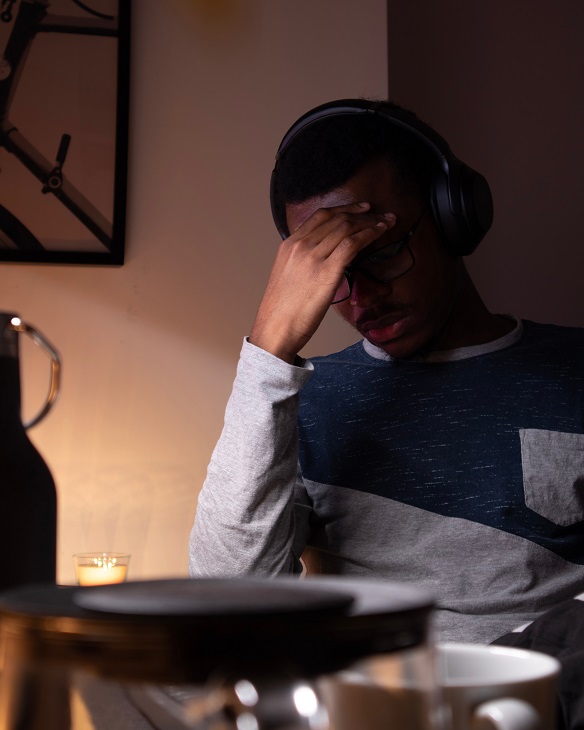
It’s morning. You can hear the world already buzzing outside and yet there you lie, struggling to throw off the covers and seize the day. Coffee is the first thing you aim for – you need it like you need air! So why are you so tired?
Like millions of other people in the world, you may be wondering: why am I tired when I wake up? This issue has plagued many people for so long, and the answer is far simpler than most people realize.
The answer to most people’s constant exhaustion is their diets. However, not many of us realize that not getting enough protein, vitamins, etc., can lead to decreased energy levels. Excessive amounts of coffee throughout the day could cause sleep issues as well – so by caffeinating to wake up, you’re really just creating a vicious cycle. The answer could even be an underlying medical issue.
In this overview, we’ll cover the multiple reasons you may be feeling tired and what you can do to fix it. We’ll also discuss the effects sleep deprivation can have on your mind and body, as well as natural remedies and supplements you could use to boost your energy levels.
Why Is Sleep So Important?
Most people don’t realize why sleep is so important for their health. You may have difficulty focusing, driving, and working after not getting a good night’s rest. Studies have shown that long-term sleep deprivation could even cause issues such as memory loss, depression, heart attacks, or even strokes. We need sleep not only to survive, but also to live our lives to the fullest.

What Are The Effects Of Sleep Deprivation?
If the main question you ask yourself each day is “Why do I feel tired?”, you may recognize the physical and mental effects of near-constant fatigue. Here are just a few effects sleep deprivation could have on you:
- Mental fatigue
- Increased risk of having a heart attack
- Depression
- Anxiety
- Weakened immune system
- Memory loss
Some Of The Common Reasons You’re Not Resting Properly
There are so many reasons you might be feeling tired despite getting a healthy amount of sleep each night. Figuring out what’s wrong may be as easy as changing what you eat, or could require you to see a doctor for a diagnosis.
Here are five things that could be causing your exhaustion.
1. Poor Diet
By not consuming enough protein, vitamins, minerals, etc., your body won’t have enough resources to produce the energy you need to function properly throughout the day. Simply consuming more green vegetables and lean proteins could boost your energy levels tenfold.
2. Excessive Stress
Most of us have something in our lives that gets us stressed out to the max, but all that stress is bad for our health. Talk therapy has been found to help overly stressed individuals sleep better.
3. Inactive Lifestyle
Not exercising because you’re tired could cause you to be even more tired. To sleep better at night, try adding a small amount of exercise at a time to your daily routine.
4. Excessive Caffeine Consumption
Too much caffeine could lead to interrupted sleep in the evenings. By reducing the amount of caffeine you consume each day, you could see a change in your energy levels.
5. Health Problems
Certain medical conditions can cause fatigue and will require a medical diagnosis before you can start receiving treatment. These conditions include iron deficiency (anemia), depression, anxiety, and heart disease, to name a few.
Are There Supplements For Energy?
So now that you know the reasons behind your constant fatigue, the next thing you may be asking yourself is how to stop feeling tired all the time. For many people, the answer is energy drinks or coffee, but as we mentioned above, excessive caffeine has been proven to worsen your sleeping problems. However, there are many supplements for energy and peptides for energy you could try to naturally increase your energy levels, such as the sleep box by Vital RX.

Are There Natural Ways To Feel Less Tired?
Now that you have an idea of why you’re constantly exhausted, you may be wondering: is there a natural way to stop waking up tired with no energy? The answer is yes! Here’s a few things you could try to boost your energy levelsnaturally.
1. Cut Out The Caffeine
Most of us start our days with a freshly brewed cup of coffee. If this were the only caffeine you consumed each day, it wouldn’t cause any issues, but most of us continue to drink coffee throughout the day. Whether we have it with lunch or just for the heck of it, an excessive amount of caffeine could lead to poor sleeping habits. Try limiting yourself to just one or two cups of coffee per day.
2. No More Naps
Napping in the middle of the day could result in less sleep in the evenings, leaving you exhausted all day long.
3. Be More Active
If you’re working a sedentary job where you sit most of the day, try taking short walks around the office a few times a day. Even this small bit of added exercise could lead to better sleep.
By altering your diet, setting sleep times, and getting more active, you could enhance your restfulness and put tired days behind you.
Featured image by Lograstudio on Pixabay