Having a healthy immune system is vital to avoiding illness and disease – but it can also be easy for your immune system to become compromised. There is little more important than diet when it comes to the health of your body’s defense system. Food fuels the immune system with the nutrients it needs to perform at its best, and if you eat the right things, you can promote overall good immune health now and for years to come. Let’s take a look at some natural foods that promote immune health.
What foods boost your immune system naturally?
Many nutritious foods can help you boost your immune system and keep yourself safe from outside pathogens. They include:
1. Citrus fruits
Citrus fruits are high in vitamin C, a nutrient that helps increase white blood cells. White blood cells are vital players in the fight against pathogens. Some of the best citrus fruits you can eat if you want to improve your immune health include:
- Grapefruit
- Oranges
- Tangerines
- Lemons
- Limes
- Clementines
The body doesn’t store vitamin C, so it’s important to incorporate fruits like these regularly into your diet.
2. Red bell peppers
Another great way to get the vitamin C you need is through red bell peppers. Bell peppers of the red variety contain three times the amount of vitamin C as one orange. If you don’t want to eat a citrus fruit every day or need variety to get your daily needs, adding some red bell peppers to your meals is a great way to accomplish that.
3. Broccoli
Broccoli contains several nutrients that can keep your immune system healthy. It has vitamins E, C, and A, and antioxidants that help reduce widespread inflammation. When there is inflammation in the body, especially chronic, it can weaken your defenses. By eating more broccoli, you can gain the nutrients your body needs to fight off pathogens and keep inflammation down when you are not contending with an illness.
4. Garlic
Garlic has been used for centuries as a flavorful addition to food and medicine. Garlic is excellent for the immune system because it contains the compound allicin. Allicin has the ability to both help the body fight off viruses and regulate the immune system for better overall functioning.

5. Ginger
Ginger is another food many people turn to when ill because of its medicinal properties. Ginger contains antibacterial and antiparasitic properties. The root vegetable is also a diaphoretic, which can help the body sweat out colds or cases of flu faster. Research has shown that ginger can reduce inflammation in the body and fight off oxidative stress, which can help the immune system to become better regulated.
6. Spinach
Spinach is a powerhouse of nutrients. It contains high levels of vitamin C, antioxidants, and beta-carotene. All these nutrients can increase the immune system’s ability to fight off infection and stay better protected against disease.
7. Yogurt
The health of the immune system and the gut go hand in hand. Roughly 80% of all immune cells are found in the stomach, so when it is healthy, the immune system generally is, too. This is why eating yogurt regularly can promote good immune health.
Yogurt contains beneficial live bacteria that help to stimulate the cells of the immune system in the gut to fight off disease effectively. As one of the best foods for immune health, the cultures in yogurt also help to keep the gut bacteria balanced in a way that improves not only immune health, but overall bodily health.
8. Almonds
Almonds contain high levels of vitamin E, which acts as an antioxidant within the body. According to research, vitamin E is one of the best nutrients for immune health because it modulates immune function. When the immune system is regulated correctly, it responds better to harmful pathogens.
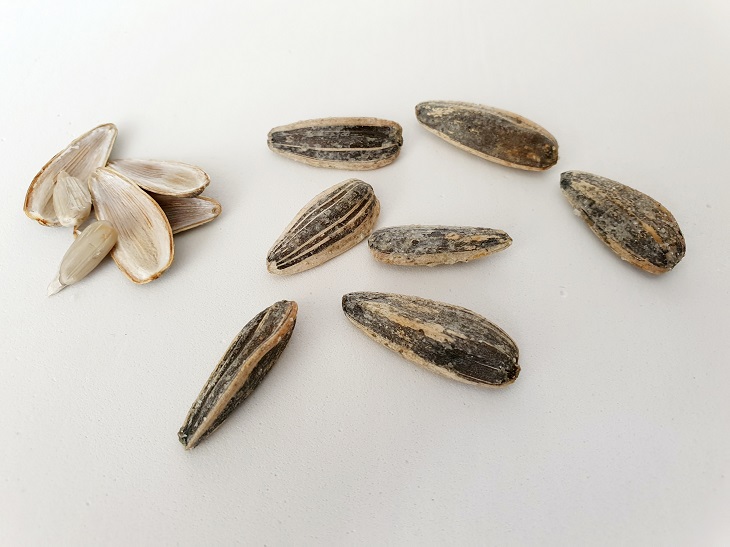

9. Sunflower seeds
Similar to almonds, sunflower seeds also contain high levels of vitamin E. Along with this nutrient, the seeds also contain selenium, phosphorous, magnesium, and vitamin B6, each of which is important to overall immune function.
Selenium acts as an antioxidant, reducing overall inflammation levels and enhancing the immune response. Phosphorous plays an essential role in immunity because of its ability to create barriers against pathogens in the body, and magnesium can strengthen the action of white blood cells. When you get enough magnesium, your immune cells can better find and destroy pathogens.
10. Turmeric
Turmeric has long been used in the natural medicine world because of its ability to combat illness and treat various types of arthritic diseases. The substance that gives turmeric its medicinal properties is curcumin. According to research on curcumin and immunity, the spice can influence how well immune cells function. That influence helps the immune system maintain readiness for fighting off infections.
11. Green tea
Green tea is another immune-friendly food touted for its health benefits. Green tea contains flavonoids, which are great for regulating the immune response. The compounds help immunity because they can inhibit the activation of specific immune cells that harm how well the immune system functions.
An antioxidant known as epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) is also found in high amounts in green tea. Research has shown that this particular antioxidant can boost the immune system.
Incorporating these foods regularly into your diet will ensure you get all the nutrients your immune system needs to keep you well protected now and in the future.
Featured image by Bruna Branco on Unsplash