Between diets that lack the appropriate nutrients to the inability to store certain vitamins in the body, getting the recommended daily dose of all the essential nutrients one needs can be a difficult task. Some vitamins, such as vitamin D, are especially important for overall health. Since the vitamin’s primary source is sunshine, the winter months pose an increased risk of deficiency.
Getting vitamin D the old-fashioned way is hindered for much of the winter season because there are less hours of sunlight, and less sunshine during cold and cloudy winter days. There’s also the common desire to avoid the cold by staying indoors much more than one might in the summer time. But how dangerous is a vitamin D deficiency, particularly in the colder months? Here’s why lack of vitamin D in the winter poses a serious threat to your health.
What is vitamin D and what does it do for the body?
Vitamin D is an essential nutrient. It is fat-soluble, which means it is synthesized within the body when the skin absorbs the sun’s rays, and then stored in fatty tissues. The nutrient is also absorbed into the body through food. Since it acts as both a vitamin and a steroid hormone, it is important for a variety of different processes throughout the body. One of the most important processes is calcium and phosphorous absorption, which helps with bone health.
Vitamin D also plays a vital role in the function of the immune system, as it acts as both an immune system regulator and moderator. It is a nutrient that the immune system relies on to ensure that the response to pathogens is initiated properly to avoid infection and illness.
Other studies have found that vitamin D has exceptional disease-fighting abilities. It can help to decrease the risk of developing cardiovascular disease and multiple sclerosis, and can even prevent the development of the flu. The essential nutrient also plays a role in mood regulation and has been known to reduce symptoms of depression.

What does it mean if you’re lacking vitamin D?
If you don’t get enough vitamin D in your system, your body becomes deficient and many of the processes that rely on the nutrient may begin to malfunction. There are many reasons that one may lack vitamin D. The amount needed will vary slightly from person to person, but there are daily recommended amounts based on age that most people should adhere to. For people aged nine and over, anywhere from 600 IU/day up to 4000 IU/day is recommended. The upper level intake is the highest amount of the vitamin that can be taken without adverse health effects.
Vitamin D deficiency can be caused by certain health conditions such as cystic fibrosis, Crohn’s disease, and celiac disease. These diseases can cause the intestines to have difficulties absorbing the nutrient if it is taken as a supplement. Weight loss surgeries, obesity, and kidney and liver diseases can also play a role in vitamin D deficiency. The body’s ability to make vitamin D also decreases with age, and those who are less mobile and thus spend less time outside all year round can also suffer from vitamin D deficiency.
Vitamin D deficiency symptoms
If vitamin D deficiency becomes severe it can cause rickets – a bone problem that affects mostly children and leads to bones that are easily bendable, breakable, and painful. Rickets can develop in adults, where it is referred to as osteomalacia. These conditions occur only in the most serious of vitamin D deficiency cases.
For those who are lacking in this essential nutrient but not yet suffering the most severe consequences, symptoms may appear to be mild in nature and include:
- Chronic fatigue
- Bone pain
- Muscle weakness, cramps, or aches
- Depression and other mood changes
- Frequent infections
- Back pain
- Wounds that don’t heal properly or are slow to heal
- Bone loss
- Hair loss
About one billion people in the world are suspected to be deficient in vitamin D, and it is one of the most commonly found nutritional deficiencies worldwide.
How to get vitamin D in winter
Getting vitamin D in winter can be tricky. Since people spend less time outdoors, the chances of a deficiency in winter are greater, thus more vitamin D may need to be introduced through other means during those cold months. A great way to keep vitamin D levels up naturally in the winter is by getting outside as much as possible. Even if it’s cold out, if the sun is shining, your body can still absorb the rays and synthesize vitamin D.
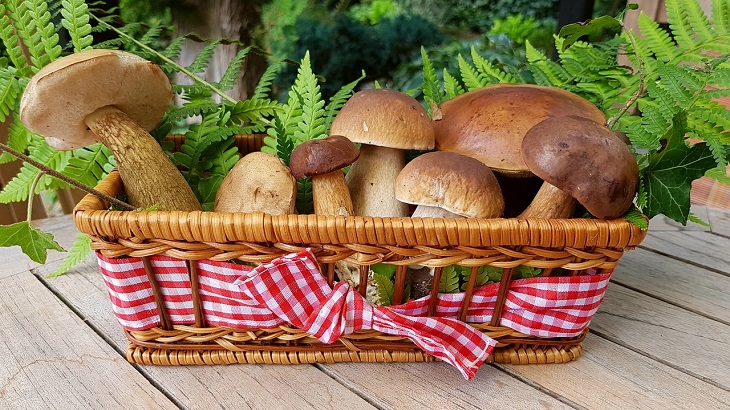
Another great way to get more vitamin D in the winter months is through diet. The best food options to get as much vitamin D as possible include:
- Pork
- Mushrooms
- Fatty fish such as mackerel, oysters, shrimp, and tuna
- Cheese
- Egg yolks
- Vitamin D-enriched foods such as orange juice, cereal, soy milk, and yogurt

You may also want to increase your intake along with your enriched diet with vitamin D supplementation. If you believe your vitamin D levels are severely low, getting a blood test with your primary care physician can let you know just how much you need to restore yourself to adequate levels. They may opt for a prescription supplement of vitamin D or recommend a good over-the-counter supplement.
Getting enough vitamin D in the winter may be difficult, but it’s not impossible. In the winter months, it is especially important to have enough of the nutrient because it can help ward off infection and chronic disease. As the winter season is typically flu and cold season, you’ll want to avoid getting sick as best you can with adequate levels of vitamin D.
Featured image by Free-Photos on Pixabay